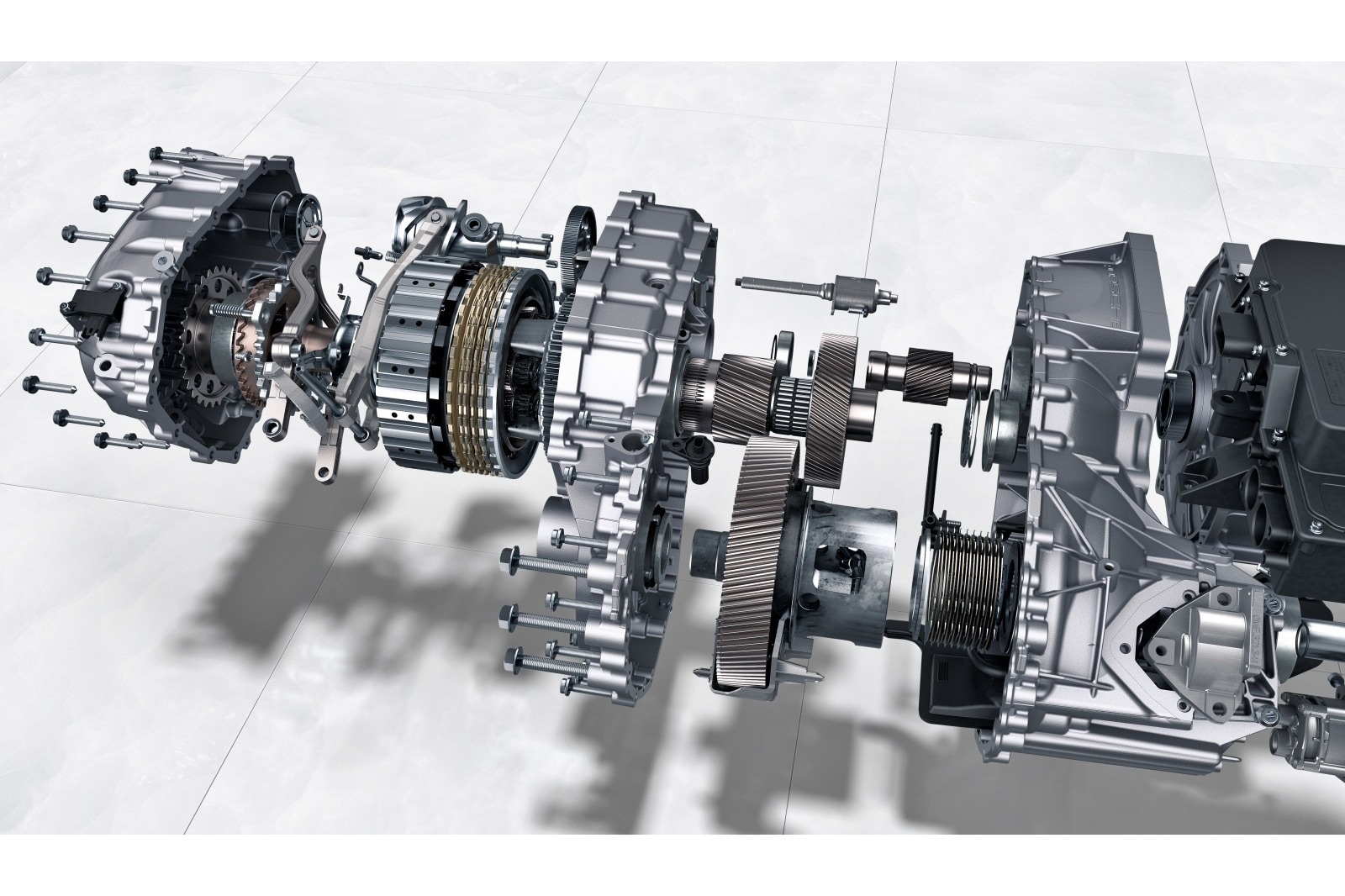
The automotive industry is shifting toward electric vehicles as a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional vehicles with internal combustion engines (also known as ICE vehicles). As with any new technology, people have questions about how electric cars work and what components they include. One of the most commonly asked questions is whether electric cars have transmissions. The short answer is, yes, electric cars do have transmissions. That said, electric transmissions differ in a number of ways from those of traditional ICE vehicles. The main difference is that most electric cars use a single-speed transmission, whereas gas-powered vehicles use multi-speed transmissions.
In this article, we'll discuss the differences between an electric vehicle transmission and a traditional transmission. We'll also take a deeper look at the powertrain of an electric car, discuss what makes EV powertrains unique, cover any variations in designs, and speculate on the future of EV transmissions. For the purposes of simplification, we won't be discussing continuously variable automatic transmissions, or CVTs, which are physically distinct from a traditional ICE transmission but also offer multiple gear ratios.