- GM will debut the next iteration of its hands-free driving system, dubbed Ultra Cruise, on the upcoming Cadillac Celestiq.
- Here's what Ultra Cruise is, how it works, and how GM plans on rolling it out safely.
- Ultra Cruise will eventually replace Super Cruise in GM vehicles.
What Is Ultra Cruise? Here's How GM's Hands-Free Driving System Works
A suite of advanced systems accompanies GM's driver assist tech
The General Motors Super Cruise system is a suite of advanced driver aids that, in certain circumstances, allows drivers to take their hands off the steering wheel if they keep their eyes on the road. Right now, this high level of assistance requires the equipped vehicle to be traveling on one of the 200,000-400,000 miles (depending on the model) of mostly highway roads throughout the U.S. and Canada that GM has already mapped out. The company wants to take Super Cruise to the next level, but what could be better than Super? Ultra, of course.
Ultra Cruise is the next step in GM's self-proclaimed "path to autonomous" and, like Super Cruise, it's designed as a Level 2 advanced driver assist system (as defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers). The plan is for GM to start the rollout of Ultra Cruise on its upcoming $300,000 electric supersedan, the Cadillac Celestiq. Other models will get the tech eventually, but GM is waiting for its next generation of products to open up Ultra Cruise to the masses.
How does Ultra Cruise work, and is it safe?
Ultra Cruise works on the same principles as Super Cruise. With Super Cruise, the vehicle's advanced safety features (including adaptive cruise control, forward collision mitigation and lane centering) tie into the navigation system, which then cross-references positioning information with GM's premapped routes. As long as what the nav and premapped routes agree (i.e., there aren't unexpected lane closures or the road hasn't changed since it was mapped) and the sensors agree it's safe, the driver can activate Super Cruise and take his or her hands off the wheel.
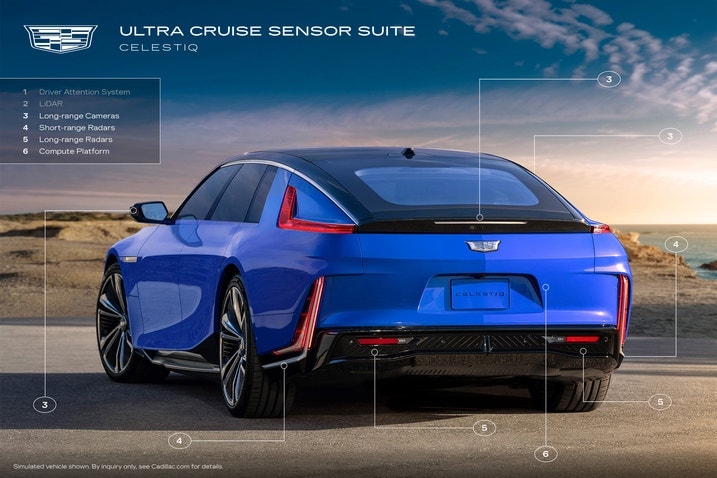
Ultra Cruise builds off Super Cruise with additional sensors (the most notable being the lidar unit behind the windshield) that feed information into an all-new computing system. GM uses sensor fusion (a fancy term that just means all the information is used at the same time) to create a 360-degree, three-dimensional map of the world around the vehicle. Here is a more in-depth summary of what each of these sensors will do, per GM:
- "Compute platform: This is the physical hardware that enables Ultra Cruise. The system will be powered by a scalable compute architecture featuring system-on-chips (SoCs) developed by American semiconductor company Qualcomm Technologies.
- "Long-range cameras: These seven, eight-megapixel cameras are located on the front, corners, back and sides of the vehicle, providing expanded fields of view for Ultra Cruise. They help enable the system to detect objects such as traffic signs, traffic lights, other vehicles and pedestrians.
- "Short-range radars: Placed on the four corners of the vehicle, these radars are used to help sense a radius of up to 90 meters, like pedestrians crossing the street or vehicles in surrounding lanes.
- "Long-range radars: The three 4D long-range radars on the front and back of the vehicle allow for Adaptive Cruise Control speeds as well as lane change maneuvers at highway speeds by helping to detect an object’s location, direction and elevation relative to the speed of the vehicle. They also help the system determine safe stopping distances.
- "LiDAR: The LiDAR, located behind the windshield, helps produce an accurate three-dimensional view of the scene, enabling more precise detection of objects and road features such as vehicles and lane markings, even in inclement weather conditions. Combined with other sensors, it can help create a robust perception of the environment around the vehicle for Ultra Cruise, increasing the system’s functional domain and performance."
The last part of the sensor array is the driver-attention system. There is a small camera that's located on the top of the steering column — right in front of the car's instrument panel — that uses infrared light to monitor the driver's head position and track the person's eyes. Cars equipped with Super Cruise currently have this tech, and it's a key piece in making sure the systems are used properly.
We can't say for certain that Ultra Cruise is safe, but according to GM, the deployment of this technology revolves around testing and validation, educating customers and working with local Departments of Transportation to take roadwork (which would naturally clash with premapped information) into account. One has to imagine GM will ship Ultra Cruise as a finished product, unlike Tesla, which labels its so-called Full Self-Driving function "beta," or not complete.
GM says the goal is to eventually "enable hands-free driving in 95 percent of all driving scenarios." Right now Super Cruise uses premapped highways and roadways to help give the system a clearer picture of what's around it at all time. We asked GM if Ultra Cruise will use the same mapping systems or if it won't need the mapping at all. A GM spokesperson told us, "Ultra Cruise will offer a destination-to-destination hands-free driving experience [...] Ultra Cruise will use the LiDAR mapping that Super Cruise has on more than 400,000 miles of highways, plus additional mapping beyond Super Cruise’s domain. Stay tuned for more details on Ultra Cruise’s mapping strategy." Which likely means even more premapped roads for Ultra Cruise when it does eventually make its way beyond the Celestiq.
Edmunds says
It might be a while, but cruising from L.A. to Tahoe with Ultra Cruise sounds pretty nice to us.






 by
by